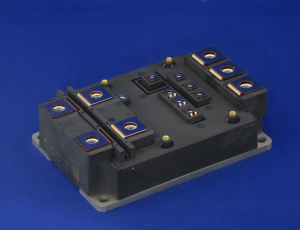
Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. announces the launch of new 7th generation X-series IGBT modules HPnC, used to maximize energy savings in rail transports.
In recent years, rail systems have emerged as an energy-efficient and ecological means of transport.
Since the operation of the railway wagon requires large amounts of electricity, it is necessary to reduce wagon equipment size and weight and increase its efficiency.
Fuji Electric has therefore developed and started manufacturing high capacity HPnC IGBT modules to reduce power loss and save energy.
Power semiconductors are electronic components that convert AC and DC power through high-speed switching (on and off). They are installed in the main inverter of the propulsion system that runs the rail cars and in the auxiliary power systems that provide energy for the air conditioning system and interior lighting.
HPnC is a 7th generation IGBT that boasts some of the best low-loss performance in the industry.
By optimizing the package structure, Fuji Electric reduced the internal inductance, which interferes with high-speed switching, by 76% compared to conventional products, resulting in low losses.
An inverter equipped with the new HPnC reduces power losses during operation by approximately 8.6% compared to the conventional product (Fuji Electric High Power Module). In addition, combined with improved heat dissipation, it reduces heat generation, resulting in a 19% size reduction and 13% weight reduction compared to the conventional product.
Fuji Electric expects the electric railway market to grow at an average annual rate of 6% in the future, reaching around 50 and 60 billion yen in 2023. For this the project is to expand HPnC IGBT modules on a global scale.
Improved reliability with overhauled substrate materials: a major cause of IGBT module failure is the deterioration of interfaces between different components due to stress caused by temperature changes during operation.
Fuji Electric has replaced the baseplate material from conventional aluminum silicon carbide (AlSiC) composite to a magnesium silicon carbide (MgSiC) composite, thereby improving heat dissipation and reducing stress caused by thermal changes.
In addition, the terminals of the new module are attached to the insulating substrate by ultrasonic bonding, instead of the solder joint in the conventional module, thus reducing the failure rate.
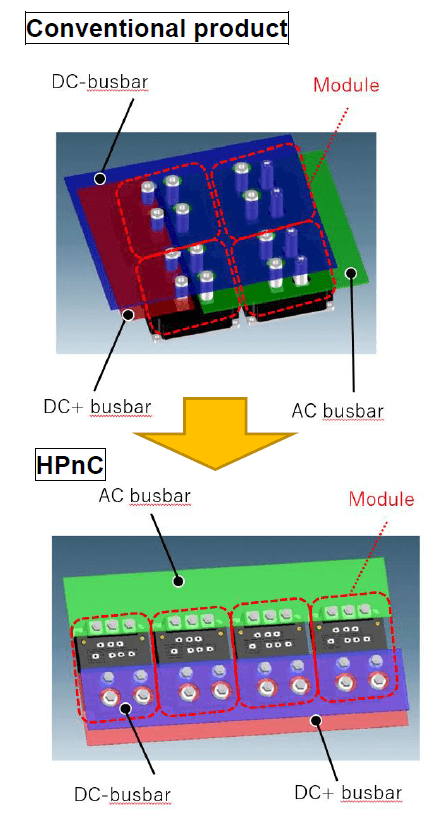
Facilitates parallel connection of power semiconductors: the conventional product requires three separate busbars (conductors for electrical connection; DC +, DC- and AC busbars) that overlap when building a circuit, making wiring configuration complicated when using parallel semiconductor connection of power.
Optimizing the terminal arrangement of this product made it possible to arrange three types of busbars in the same direction, easily facilitating parallel (multiple) connection of power semiconductors and helping to improve the assembly of various inverters.